Many people assume that deteriorating hearing is simply an inevitable part of growing older and nothing can be done about it. Age-related changes do affect hearing, but dismissing all hearing difficulties as a natural ageing process can mean missing serious underlying conditions that need proper assessment and treatment.
Consulting an ear nose and throat specialist provides comprehensive diagnostic evaluation that goes far beyond basic hearing checks. ENT specialists use advanced imaging, microscopy, and specialised testing to identify the exact cause and type of hearing impairment, revealing whether treatment can restore hearing function or whether supportive management is needed.
Understanding Different Types of Hearing Loss
Conductive Hearing Loss Explained: This type occurs when sound waves cannot travel efficiently through the outer or middle ear to reach the inner ear. Common causes include earwax buildup, fluid accumulation behind the eardrum, perforated eardrums, or problems with the tiny bones in the middle ear.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss Characteristics: This involves damage to the inner ear structures or the auditory nerve pathways to the brain. Age-related changes, prolonged noise exposure, certain medications, head injuries, and various medical conditions can cause sensorineural hearing loss that typically cannot be reversed completely.
Mixed Hearing Loss Patterns: Some individuals experience both conductive and sensorineural components simultaneously. Perhaps someone with age-related nerve changes develops a middle ear infection, or longstanding fluid problems occur alongside noise-induced damage. Identifying each component guides treatment decisions about which aspects might improve with intervention.
Specialist Assessment vs General Hearing Tests
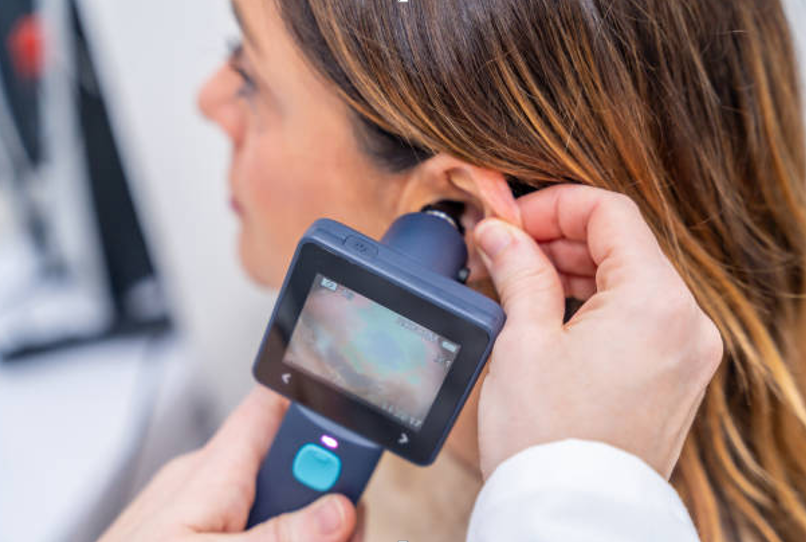
Comprehensive ENT Examination Process: Specialist evaluation begins with detailed history-taking about symptom onset, progression patterns, associated problems like tinnitus or balance issues, medication history, and noise exposure. Otoscopy examination uses specialised instruments to inspect the ear canal and eardrum thoroughly, identifying blockages or structural problems.
Advanced Diagnostic Testing Available: ENT specialists arrange pure tone audiometry that tests hearing thresholds across different frequencies, speech discrimination testing that assesses understanding ability, tympanometry that measures middle ear function, and acoustic reflex testing. When indicated, specialists request temporal bone CT scans or MRI imaging.
Differentiating Medical Conditions: Many treatable conditions present with hearing loss as a primary symptom. Otosclerosis causes progressive hearing loss from abnormal bone growth affecting the middle ear. Cholesteatoma creates expanding cysts that damage ear structures, whilst Ménière’s disease causes fluctuating hearing loss with vertigo episodes requiring specialist management.
Treatment Options Beyond Hearing Aids
Medical Management Approaches: When hearing loss results from infection, inflammation, or fluid accumulation, appropriate medications often improve hearing substantially. Antibiotics treat bacterial infections, steroid treatments reduce inflammatory swelling, and decongestants help clear Eustachian tube blockages that affect hearing and cause discomfort.
Surgical Intervention Possibilities: Various surgical procedures address specific causes of hearing loss effectively:
- Tympanoplasty repairs perforated eardrums using grafts, restoring the protective barrier and improving sound transmission mechanisms.
- Ossiculoplasty reconstructs or replaces damaged middle ear bones, re-establishing the mechanical sound conduction pathway properly.
- Stapedectomy treats otosclerosis by replacing the fixed stapes bone with a prosthetic device that conducts sound properly.
- Cholesteatoma removal prevents progressive damage and often improves hearing once disease tissue is completely excised surgically.
Hearing Rehabilitation Strategies: When hearing cannot be restored medically or surgically, various amplification and assistive devices improve communication function significantly. Modern hearing aids offer sophisticated sound processing tailored to individual hearing patterns, whilst bone-anchored hearing systems bypass damaged middle ears by transmitting vibrations through skull bones.
When Delays Create Permanent Problems
Progressive Damage from Untreated Conditions: Delaying specialist assessment allows certain conditions to cause irreversible damage that could have been prevented with timely intervention. Chronic infections erode delicate ear structures, cholesteatomas expand destructively, and prolonged conductive problems sometimes lead to permanent sensorineural changes affecting nerve function.
Impact on Quality of Life: Unaddressed hearing loss significantly affects social interaction, emotional wellbeing, cognitive function, and safety awareness. Communication difficulties lead to social withdrawal, relationship strain, workplace challenges, and increased accident risks. Early specialist intervention prevents these cascading problems from developing.
See also: Do I Need, Study Abroad Medical Insurance? Everything Students Should Consider
Warning Signs Requiring Specialist Evaluation
Sudden Hearing Loss Urgency: Rapid hearing deterioration over hours or days constitutes a medical emergency requiring immediate specialist assessment. Sudden sensorineural hearing loss sometimes responds to urgent steroid treatment, but only when started within days of onset, making prompt consultation absolutely critical.
Progressive Unilateral Hearing Loss: Hearing loss affecting predominantly one ear rather than both equally deserves thorough investigation to exclude serious underlying conditions. Acoustic neuromas, other tumours, or unusual infections can present initially with one-sided hearing changes requiring specific diagnosis and monitoring.
Associated Symptoms Requiring Investigation: Hearing loss accompanied by persistent tinnitus, balance problems, facial weakness, ear discharge, or pain suggests specific underlying conditions needing specialist diagnosis. These combinations indicate problems affecting multiple ear structures or adjacent nerves requiring comprehensive assessment rather than simple hearing tests.
Conclusion
Attributing all hearing difficulties to normal ageing risks missing treatable conditions that specialist evaluation readily identifies. Comprehensive ENT assessment distinguishes between different hearing loss types, uncovers underlying medical causes, and guides appropriate treatment decisions based on accurate diagnosis. If you’ve noticed hearing changes, unexplained difficulties understanding conversation, or persistent ear symptoms, arrange specialist evaluation to explore all available treatment options rather than accepting progressive hearing deterioration as inevitable.